Calculate Molarity of Acid in Titration
In this video I am going to show you how to write a neutralization reaction and how to calculate the molarity of acidbase in order to neutralize the soluti. Determine the number of moles of H.

Molarity Calculation Of An Acid When Titrated With A Base Youtube
NH Vx Mx nOH Vy My.
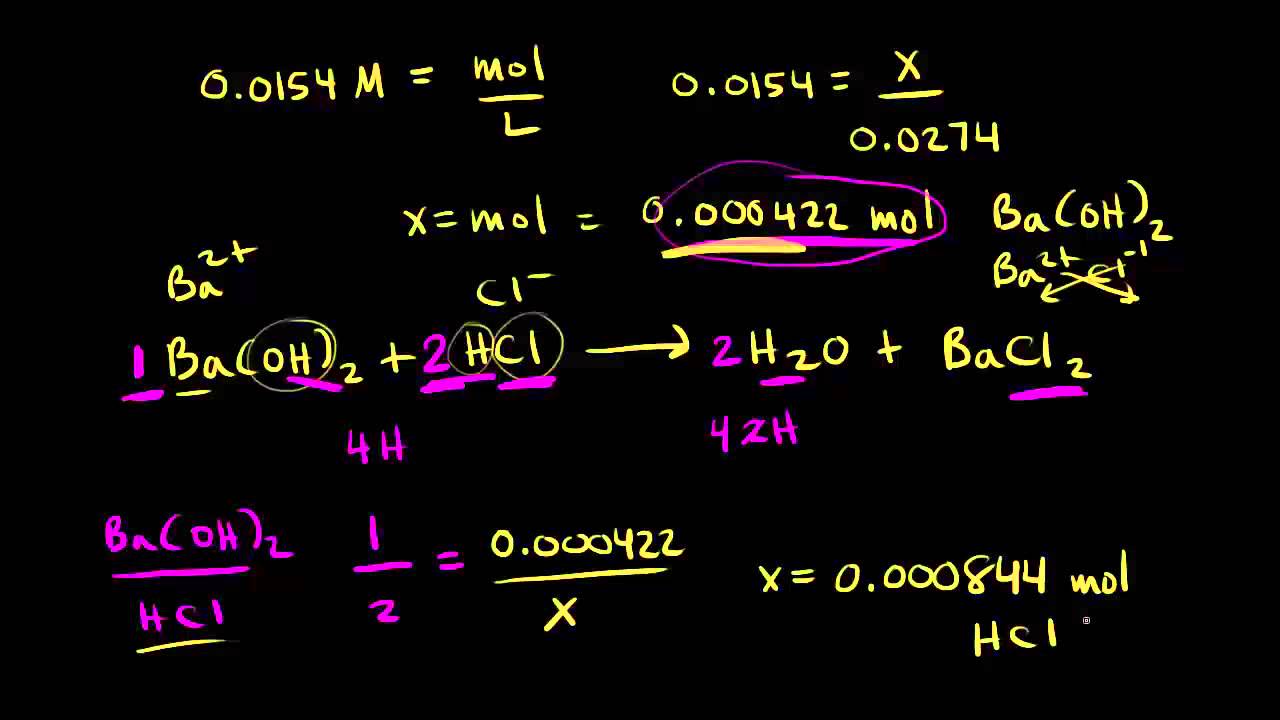
. NH Molarity acid Volume acid nOH Molarity base Volume base Where. OH- 00015 mol0065 L 0023 molL so. You will have 00015 mol of OH- in 65 mL of solution.
Point in titration at which the amount of titrant added is just enough to completely neutralize the analyte solution. Diagram of equivalence point. If the end point in the titration of oxalic acid with NaOH solution is super-passed too pink will the molar concentration of NaOH be hiegher or lower than the actual value.
Then calculate the pOH and the pH. NH is the concentration of H. Use the titration formula.
Calculate the molarity of an acetic acid solution if3457 mL of this solution are needed to neutralize 2519 mL of01025 M sodium hydroxide. N_Hn_OH- Note that the relationship between molarity and number of mole is. Therefore we can say that 1 liter of Sulfuric acid contains 17822 moles or in other words molarity of 95 ww Sulfuric acid is equal to 17822 M.
Determine molar changes use IRF table To determine molar changes convert concentration. At the equivalence point the number of mole of H ions will be equal to the number of mole of OH- ions. Titrations are used to determine the amount of one substance present by reacting it with a known amount of another substance.
Acid Formula Molar Mass pK a Application Acetic Acid CH 3CO 2H 6005 474 Vinegar Benzoic Acid C 7H 6O 2 12212 420 Food Preservative Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate KHP C 8H 5O 4K. 750 x 10 -3 mol HCl 0250 mol HCl L 00300 L HCl 300 mL HCl. Use the titration formula.
How do you find the molarity of a titration problem. How do you find moles in a titration problem. Calculate the Molarity.
This is a strong acidstrong base titration. CH3COOHaq NaOH aq width30 height13Naaq CH3COOH-aq H2O l Strategy. Tiprobes and althrometa molecules containing a 11 mole ratio should have a molarity M equal to the acid equivalent V x volume x volume s titrant and analyte have a 11 mole ratio the formula is molarity M of the In a solution.
Table 1 Data Equation calculation Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Mass KHP used g 101g 102g 101g Molar mass of KHP gmol. Determine acidbase reaction type. Rearranging the equation of molarity M molL to solve for volume gives.
Titration reactions are just neutralization reactions. D Density or specific gravity. MW Molecular Weight or Formula Weight.
Vb volume of the base. M MolsL Where M is the molarity or concentration in a solution. Mathrm H aq mathrm OH- aq longrightarrow mathrm H_2O l Step 2.
If the titrant and analyte have a 11 mole ratio the formula is molarity M of the acid x volume V of the acid molarity M of the base x volume V of the base. Titration of a base with an acid Problem. At the equivalence point in an acid-base titration moles of base moles of acid and the solution only contains salt and water.
Mx molarity of the acid. Acid-Base Titration Solution Molarity M is moles per liter of solution so you can rewrite the equation to account for molarity and volume. Determine OH- Step 2.
How to calculate titrations. Assuming additive volumes what will be the molarity of the solution that results when 355 mL of 200 M HNO3 is added to 2145 mL of water. The following equation is used for calculating acid and base molarity where the concentration is given in wt.
D MW 10 Molarity Where. For instance you can find the molar mass of an acid by titrating the acid with a solution of base of known concentration. Molarity is the concentration of a solution expressed as the number of moles of solute per litre of solution.
To find the molar mass of potassium hydrogen phthalateKHC 8 H 4 O 4 the atomic mass of each element was added together. For example after 40 mL of base you will have added 0004 mol of OH- but 00025 mol will have reacted with the acid. Determine the concentration of HCl.
K39 gmol H1 gmol O16 gmol 39 gmol 5 1 gmol 8 12 gmol 4 16 gmol 204 gmol. Acid-base titrations are monitored by the change. Figure out how many moles of the titrant in this case the base were needed.
The average molarity for this value came out to be about 0 moles per liter of solution. Determine the number of moles of OH-. Up to 24 cash back calculate molarity.
The formula used is. Use the titration formula. L mol M.
NH number of H ions contributed. Moles being the amount present of x chemical dissolved and L being liters or total volume of solution in liters. Calculate the excess moles divide by the volume to get the molarity.
In a titration a 2500 mL sample of sodium hydroxide solution was neutralized by 3272 mL of hydrochloric acid. Considering the analyte is an acidic solution unknown molarity and that it will be titrated using a basic solution with a known molarity assuming monoprotic acid and base. If the titrant and analyte have a 11 mole ratio the formula is molarity M of the acid x volume V of the acid molarity M of the base x volume V of the base.
After the titration is performed the measured values are put in a formula to find the molarity of the substance. NH number of H ions contributed per molecule of acid Ma molarity of the acid Va volume of the acid nOH number of OH - ions contributed per molecule of base Mb molarity of base and. Molarity is the concentration of a solution expressed.
1 gram of H2SO4 will be equal to 19808 moles. What is the molecular weight of an unknown. By adding known molarity of acid or base titrant and measuring the amount required to effect this change the titration calculator can calculate the molarity of the unknown value using the following weak base strong acid titration formula.
Weight. The above equation can then be used to calculate the Molarity of the 70 wt Nitric Acid. If the titrant and analyte have a 11 mole ratio the formula is molarity M of the acid x volume V of the acid molarity M of the base x volume V of the base.

11 8 Acidbase Titration The Titration Of An
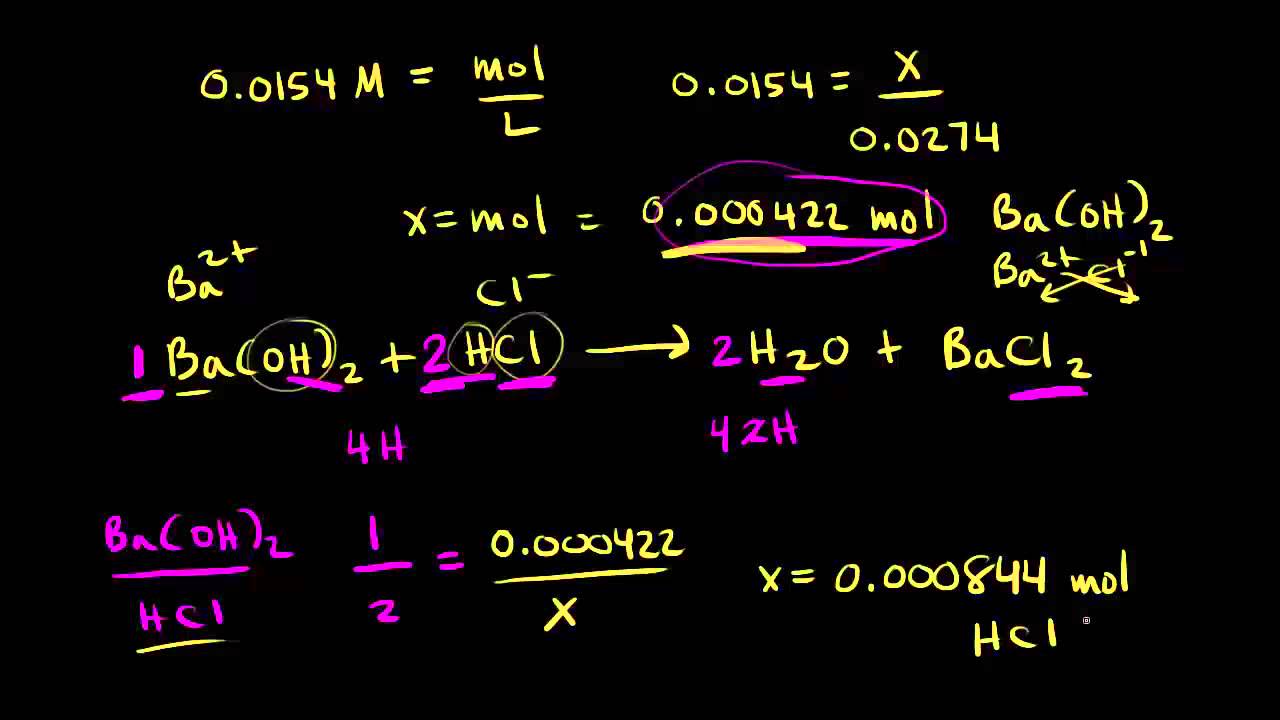
Determining Solute Concentration By Acid Base Titration Worked Example Video Khan Academy

Acid Base Titration Problems Basic Introduction Calculations Examples Solution Stoichiometry Youtube
Comments
Post a Comment